The Ultimate Guide to Arthritis:
Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Introduction
Arthritis is a prevalent condition
affecting millions worldwide, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
Despite its widespread impact, many remain unaware of its causes, symptoms, and
management techniques. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of
arthritis, offering well-researched insights into its various types, risk
factors, and effective treatments. Whether you're personally dealing with
arthritis or seeking information to support a loved one, this resource will
equip you with practical strategies to alleviate pain and maintain joint
health.
The word "arthritis"
refers to inflammation of the joints. It is not a single disease but rather a
group of over 100 related conditions that affect joints, surrounding tissues,
and other connective structures. While arthritis can impact individuals of any
age, it is more common among older adults. The condition can cause significant
discomfort and interfere with daily activities due to chronic pain and
restricted movement.
Common
Types of Arthritis
1. Osteoarthritis (OA)
- The most widespread form of arthritis.
- Develops due to the gradual degeneration of joint
cartilage.
- Commonly affects the knees, hips, hands, and spine,
leading to pain and stiffness.
2.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- An autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints.
- Leads to chronic inflammation, pain, and potential joint deformity.
- Often impacts joints symmetrically on both sides of the body.
3.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
- Occurs in individuals with psoriasis.
- Causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Can result in severe joint damage if left untreated.
4.
Gout
- A form of arthritis caused by excessive uric acid buildup in the joints.
- Typically results in sudden, intense pain, swelling,
and redness, often in the big toe.
5.
Fibromyalgia
- A long-term illness marked by painful spots, exhaustion, and generalized pain.
- Often accompanied by sleep disturbances and cognitive
issues.
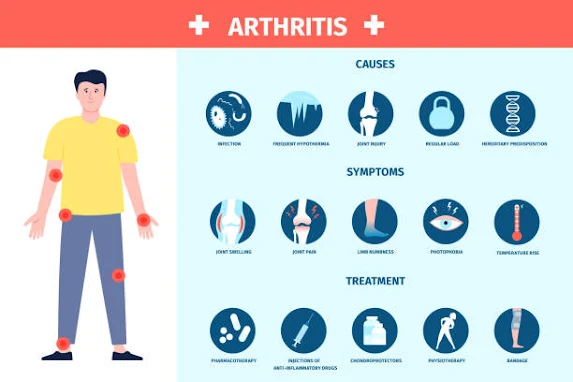
Symptoms
of Arthritis
Although symptoms vary by arthritis
type, common indicators include:
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: Persistent discomfort in affected joints.
- Swelling and Redness:
Inflammation can lead to visible swelling and tenderness.
- Fatigue:
Chronic tiredness is common among arthritis sufferers.
- Reduced Mobility:
Joint stiffness and pain can limit movement.
Causes
and Risk Factors
- Genetics:
A family history of arthritis increases susceptibility.
- Age:
The risk of arthritis rises with age.
- Obesity: Carrying
too much weight strains joints, especially the hips and knees.
- Previous Injuries:
Past joint injuries may lead to arthritis over time.
- Infections:
Certain infections can trigger arthritis in susceptible individuals.
Effective
Strategies for Managing Arthritis
1.
Medications
- Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen and
acetaminophen.
- Prescription medications, including disease-modifying
antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for RA.
- Corticosteroids and biologics for severe cases.
2.
Physical Therapy
- Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, and yoga.
- Strengthening routines to enhance joint support and
function.
3.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Maintaining a healthy weight to ease joint
stress.
- Following an anti-inflammatory diet rich in
omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol intake.
4.
Alternative Treatments
- Acupuncture:
May help reduce pain and improve flexibility.
- Massage Therapy:
Can alleviate stiffness and enhance relaxation.
- Supplements:
Glucosamine, chondroitin, and turmeric may support joint health.
Preventive
Measures
Although arthritis may not always be
preventable, adopting healthy habits can reduce the risk:
- Stay Active:
Engage in regular exercise to strengthen muscles and maintain joint
function.
- Protect Your Joints:
Use proper lifting techniques and ergonomic tools.
- Follow a Nutrient-Rich Diet: Prioritize anti-inflammatory foods to support overall
joint health.
Conclusion
Arthritis is a complex yet
manageable condition. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and
implementing effective treatment strategies, individuals can significantly
improve their quality of life. If you experience persistent joint pain, consult
a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized management
plan.
Call
to Action
- Consult a Medical Professional: If you suspect arthritis, seek early medical
intervention.
- Adopt a Joint-Friendly Lifestyle: Stay active, eat healthily, and maintain an optimal
weight.
- Explore Treatment Options: Consider both conventional and holistic approaches for
effective relief.
Author’s
Note
Thank you
for taking the time to explore this comprehensive arthritis guide. As an
advocate for health and wellness, my goal is to equip you with accurate,
research-backed, and actionable knowledge to help you take charge of your
well-being. Arthritis may present challenges, but through awareness, proactive
measures, and lifestyle changes, you can regain an active and pain-free life.
Knowledge is your greatest asset—stay informed, make conscious health choices,
and prioritize your well-being. You are worthy of experiencing life to the
fullest.